Il radiante (rad) è una unità di misura per gli angoli: è uguale a to 180°/π, così che l'ampiezza di un angolo di 180° può essere espressa come "π radianti". Spesso la parola "radianti" è omessa, per cui quando l'ampiezza di un angolo è espressa senza un'unità di misura si intende che sia rappresentataa in radianti: dire che un angolo è di 90° equivale a dire che la sua ampiezza è π/2.
The radian (rad) is a unit for measuring angles: it is equal to 180°/π, so that the magnitude of an angle of 180° can be expressed as "π radian". Often the word "radian" is omitted, as it is implied that when the amplitude of an angle is expressed without a unit of measurement it is represented in radians: saying that an angle is 90° wide is equivalent to saying that it is π/2 wide.

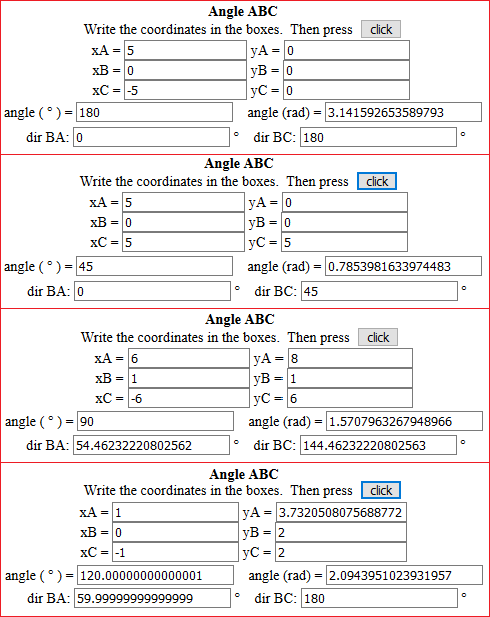
The values are rounded. In the last example yA is 2+√3. The exact value of the angle [of dir BA] is 120° [60°].
I valori sono arrotondati. Nell'ultimo esempio yA è 2+√3. Il valore esatto dell'angolo [della direzione di BA] è 120° [60°].
| How to find the slope angle of an uphill road with a gradient of 0.5 (50%), 1 (100%), 2 (200%)? Come trovare l'angolo di inclinazione di una strada in salita con pendenza 0.5 (50%), 1 (100%), 2 (200%)? |
 |
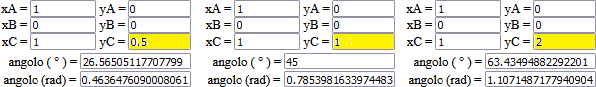
You can also use the "calcolatrice" HERE and calculate atan(0.5),
atan(1), atan(2) (enter 0.5, 1 or 2 and click [atan]).
Puoi anche usare la calcolatrice presente QUI e calcolare atan(0.5),
atan(1), atan(2) (metti 0.5, 1 o 2 e clicca [atan]).