The [N] key generates the numbers 1, 2, ..., N, which you can then transform with the [data ...] keys if you want. An example.
With [N] I generate 1, 2, ..., 20.


With 3 in [Q] and [data^Q] I get the outputs:
1, 8, 27, 64, 125, 216, 343, 512, 729, 1000, 1331, 1728, 2197, 2744, 3375, 4096, 4913, 5832, 6859, 8000
which I then copy in the box with [copy]:

I add up these numbers:

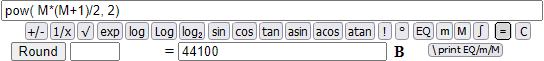
If N = 20 1³+2³+...+N³ = 44100. I verify that the same value I get with (N·(N+1)/2)².